GUID Partition Table
GPT is a new way to handle a file system that could possibly replace the older standard MBR. It should be used on an UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) system, although some BIOS (Basic Input Output System) system do support GPT file systemFeatures
GPT superseded MBR with the following features:
- GPT breaks the MBR partition limit of 2 TiB to virtually unlimited 18 EB (~18,000,000 TB)
- GPT allows up to 128 primary partitions to be made
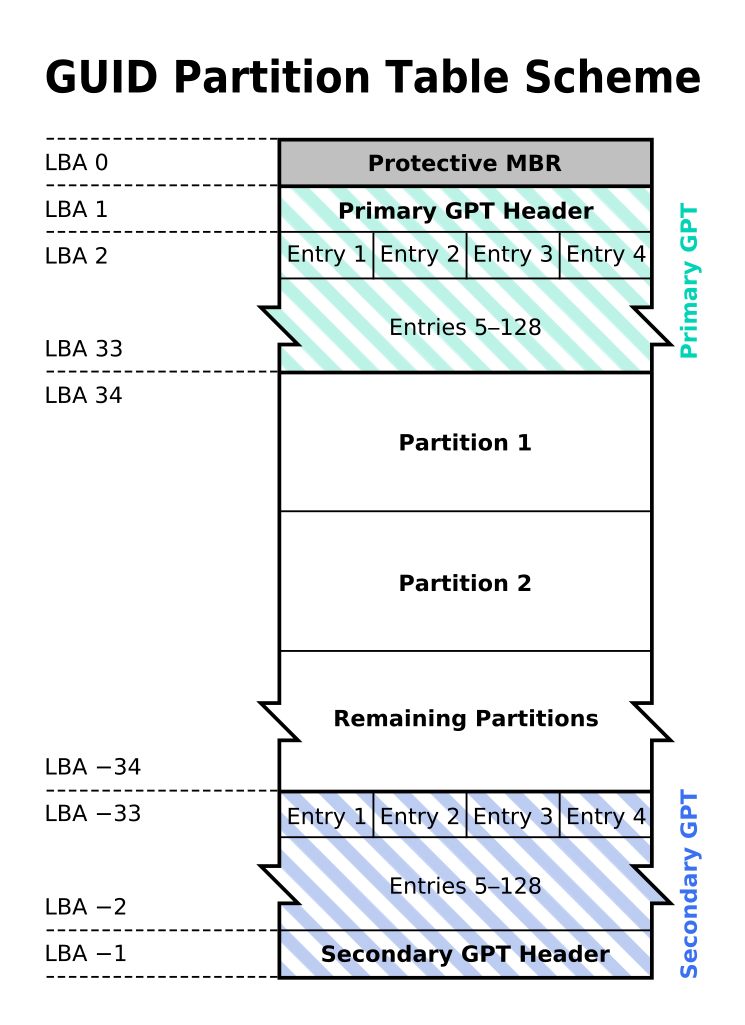
- A protective MBR sector will be located at sector 0, the most front of the partition to prevent MBR-only operating system mistaken the the GPT as unpartitioned and overwrite everything in the GPT
- It stores critical files on after the protective MBR and end of partition to increase redundancy
- It contains cyclic redundancy check (CRC) to check for corrupted files and attempt to repair it
Compatibility
Most newer versions of operating systems supports reading and writing file on a GPT file system.Support both read/write and booting from GPT (BIOS and UEFI):
- Windows Vista and 7 (64 bit only), 8, 8.1 and 10 (32 bit and 64 bit)
- Windows Server 2003 (IA-64), 2008, 2008 R2, 2012 and 2016 (IA-32)
Complete support for GPT:
- Windows Server from 2003 to 2016 that uses IA-64 architecture
- OS X since 10.4 (Only for Intel Macintosh Computer)
- Linux, Fedora since version 8 and Ubuntu since version 8.4
- FreeBSD since version 7.0
- Solaris since Solaris 10
This article is referred from Wikipedia's GUID Partition Table article.